| Air Medical Trainings & Lectures |
History of Air Medical Transport
- The hot air balloon period.
- Transport by bi-plane without observation.
- Multi transport by remodeled military airplanes.
- Transport by helicopter during war times.
|
|
Operations
- Important insurances to have.
- Choice of medical personnel according to qualification and scope of care.
- Medical crew introduction.
- Initial training programme.
- Necessary medical equipment.
- Medication. How much to order, how to stock, how to check easily.
- Fit-to-Fly or Evacuation? Impact on choice of aircraft and composition of crew
- Familiarisation with pilots' workload and duty times.
- Familiarisation with airplane and emergency equipment.
- Loading of the equipment. What to keep where.
- Safe loading and unloading of a patient.
- Procedures in the cabin. Your role in between of cabin crew and medical passenger.
- Communication with the office, the insurance/assistance company, the referring and receiving hospitals, and the ground ambulance companies.
- Documentation requirements.
- Travel documents, visa, vaccinations, health checks.
|
|
Altitude Physiology
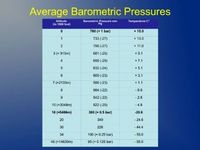
- The atmosphere.
- The gas laws with calculations.
- The gas laws and the human body.
- The gas laws and your equipment.
- The stressors of flight influencing your functionality.
- The stressors of flight influencing patient health.
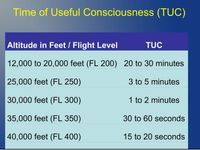
- Pressurisation and (rapid) decompression, TUC.
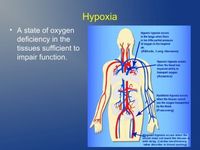
- The different types of hypoxia.
- Decompression sickness.
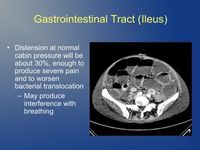
- How to counteract the negative effects of flying on your patient.
- The different environmental conditions for patients in bigger airplanes compared to smaller jets.
|
|
Intensive Care / Critical Care Transfers
- Necessary qualification of personnel for safe transfers.
- Necessary equipment.
- The importance of working space.
- Which information to collect before flying?
- Which communication to be done before flying?
- Which medical procedures to be done at which phase of the transfer.
- Necessary standard of ground ambulances.
- Documentation.
- Legal aspects.
|
|
Mechanical Ventilation
- Basics of oxygenation and ventilation.
- Basic settings of a mechanical ventilator.
- Advanced settings of a mechanical ventilator.
- Different (international) ventilator modes and how they differ.
- Actual ICU ventilation modes.
- What you can see from ventilation curves and loops.
- The importance of capnography, even in non-ventilated patients.
- Critical care transport ventilators and their specifications.
- Which critical care transport ventilators function well at altitude?
- Which critical care transport ventilators can ventilate a sick lung?
|
|
Flight Nursing and Flight Physiotherapy
- Procedures to be done frequently.
- Physiotherapy even in small cabins.
- How to fight the effects of third spacing.
- How to perform procedures without losing lines.
- The positive effect on yourself working on and with the patient.
|
|
Hygiene - Precautions
- Which vaccinations are a must, which are recommended?
- The problem with Malaria and chemoprophylaxis.
- The actual travel medical situation for Malaria.
- The actual travel medical situation for Yellow Fever.
- The actual travel medical situation for Typhoid Fever, Meningitis, Dengue, Chikungunya, Zika, MERS, and the dangers for us.
- Professional behaviour to prevent food poisoning while on a mission.
|
|
Hygiene - Flying an Infectious Patient
- Ways of transmission.
- Proper procedures for hand hygiene.
- Procedures to minimise the risk of getting infected or spreading the germ.
- Are the pilots at risk?
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE).
- How to protect yourself and the pilots and still have a workable situation.
- Disinfection of equipment and cabin.
- Documentation.
- Communication (personnel, hospitals, ground ambulances, airport employees).
|
|
Hygiene - Multi Resistant Germs
- Classification of bacteria, spores and toxins.
- Colonisation location and precautions.
- How are they transmitted? Specific necessary PPE to prevent transmission.
- Survivability of germs on surfaces.
- Dangers to transfer personnel depending on situation in referring hospital.
- Countries with high rates of and specific strains of multi resistant germs.
|
|
Resuscitation (including First Aid Training for Pilots)
- The latest guidelines from October 2021
- Basic Life Support
- Advanced Life Support
- Automated External Defibrillator
- The incapacitated pilot
- (Near) drowning
- Allergic shock
- The typical signs of myocardial ischaemia during flight compared to on the ground.
|
|
Trauma Management
- Initial assessment and stabilisation.
- Difficult airway and helpful equipment.
- The danger of ARDS and how to ventilate the trauma patient.
- Thoracic drainage placement for pneumothorax or hematothorax.
- Dealing with traumatic brain injury.
- Trauma induced coagulation disorders.
- Basics on fracture stabilisation.
- Lab results and what to correct before flight.
- The importance of blood gas analysis even in non-ventilated patients.
- What is still in some national guidelines but harms the patient?
|
|
Burns Management
- Estimation of degree and surface percentage.
- When breathing difficulties must be expected.
- Wound cover.
- Fluid management.
- Pain management.
- Positioning during flight.
- Choice of hospital (flight time vs expertise).
|
|
Medical Diagnoses and Air Medical Transfer
- Depending on the diagnosis, the treatment and the time since onset or treatment, a patient should not be flown, may have to be flown by air ambulance or may be flown by commercial airliner with or without a medical escort. We point out the options.
|
|
The Psychiatric Patient
- Which are the "trouble" diagnoses?
- When do you need a legal guardian?
- Correct way of consenting to air medical transfer.
- What are the laws when you want to sedate a patient?
- What are your rights?
- When is physical or pharmacologic fixation legally allowed?
- Who is responsible at selective locations?
|
|
Ground Ambulance Transport
- The most dangerous part of the patient transfer.
- What to check when ordering a ground ambulance?
- What to check before entering a ground ambulance?
- What to check after having boarded a ground ambulance?
|
|
Air Medical Resource Management
- The history of CRM and its' limitations.
- The evolution of CRM.
- Cultural differences in CRM - aviation compared to medicine.
- The evolution to Air Medical Resource Management
- The single steps towards a good functioning team.
- No team player? No flight!
|
|
Quality System
- How to install a quality system?
- Who should participate in which stage?
- Which medical data to collect?
- Which operational data to collect?
- Feedback from whom and how?
- Case review and analysis.
- Written procedures and their necessity for quality.
- How to analyse the data?
- Quality meetings and the aim of improving.
- The circle of improvement.
|
|
Ditching and Surviving in the Cold
- How to prepare the cabin before ditching?
- Where to position necessary safety equipment?
- How to prepare the patient?
- How to position yourself before ditching?
- What to do when after ditching?
- How to find the exit?
- How to stay as warm as possible in the water?
- How to enter the life raft?
- How to use survival equipment?
|
|
Smoke and Fire in the Cabin
- How to detect and find a fire in the cabin?
- What is the main origin of fire and smoke in the cabin?
- Specific roles of the medical team in case of fire.
- What to prepare before attempting to fight the fire?
- How to approach a fire?
- How to use the axe?
- How to use the fire extinguisher?
- Different kinds of fire extinguishers and important things to know.
|
|
Hazardous Materials
- Different classes of hazardous materials and examples.
- What are the hazardous materials we encounter during our work?
- What are the health threats of the hazardous materials we encounter?
- What is the treatment when exposure occured?
- How to deal with biological and potentially infectious waste?
|
|
Aviation
- Aerodynamics.
- Parts of the airplane.
- Function of a jet engine.
- Air intake and pressurization.
- Pitot tube and static vent.
- Instruments in the cockpit.
|
|
Meteorology
- The climatic zones of the earth.
- Low pressure and high pressure areas and the generation of wind.
- The Coriolis effect.
- Fronts and specific weather phenomena.
- Local weather phenomena.
- Cloud types and their specifications.
- Where to expect turbulences, including CAT.
- Aviation weather reports and forecasts explained (METAR, TAF).
|
|
Legal Aspects - National medical certification
- Registration of aircraft
- Countries underneath
- Departure & arrival country
- Who is responsible for the patient at which location?
- Consenting, legal guardian
- Aviation laws
|
|
tel. +31 46 3690126 service@glo-bal-med.com
Globalmed Air Medical Services B.V.
Horsterweg 27, 6199 AC Maastricht Airport, Netherlands